2.2 Renewable Energies
2.2 Renewable Energies
This chapter discusses renewable electricity as the central raw material for green hydrogen production. It highlights the three origins of renewable energy: geothermal heat, solar energy, and gravity. Technologies such as photovoltaic systems, wind turbines, and hydropower plants are used to generate renewable electricity. Hydropower and biomass have limitations, making photovoltaic systems and wind turbines the main options for large-scale green hydrogen production.
Wind energy turbines
Modern wind turbines slow down the wind and extract energy from the flowing air mass with the help of rotor blades. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind first into mechanical energy (the rotation of rotor system) and then into electrical energy. However, it is physically impossible to extract all the energy from the wind: if we would extract all kinetic energy, the wind speed would become zero and then the path would be blocked by the non-moving air while the moving air would just go around the wind turbine so that no energy can be extracted any longer. Thus, a wind turbine can theoretically convert a maximum of 59.3 % of the wind power into mechanical power at the rotor. This ratio of extractable power to maximum wind capacity is described by the so-called Betz's coefficient.
- Rotor blades
- Rotor hub
- Generator
- Power train with brake (and gear)
- Wind sensors
- Yaw drive
- Nacelle
- Tower
- Foundation
- Grid connection
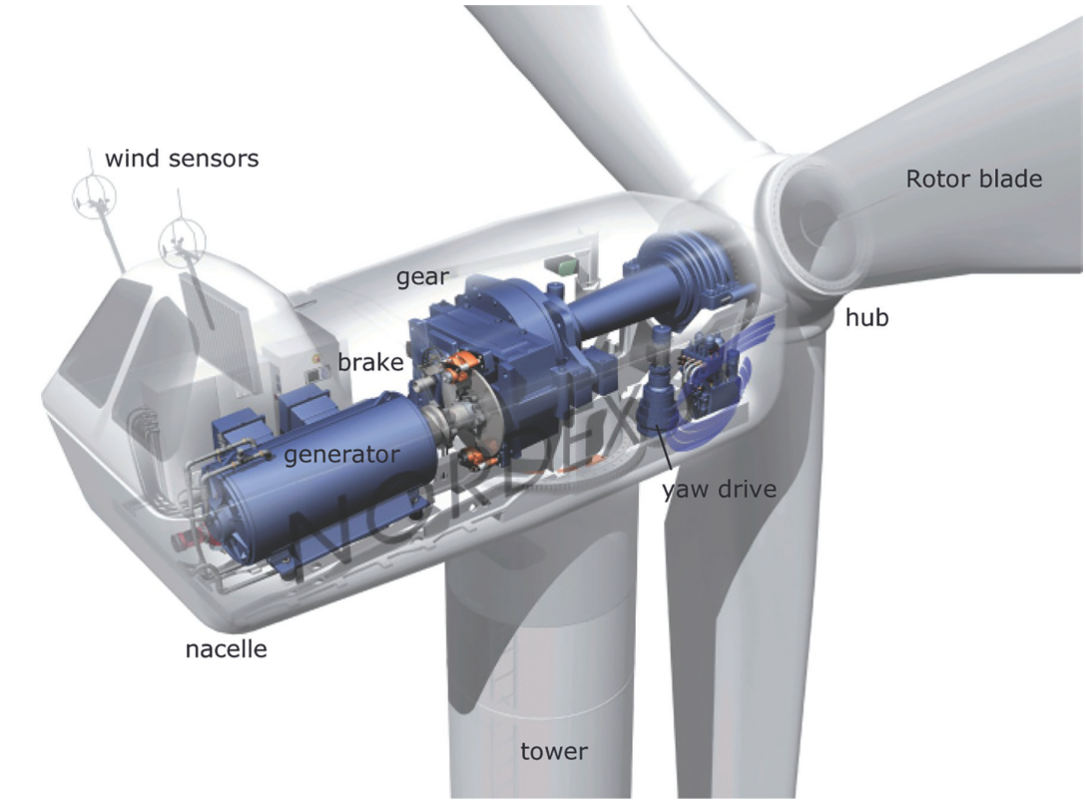
In addition to the limitation of the usable wind energy indicated by the Betz's coefficient, the energy conversion in the generator and, if present, the gear also lead to relevant losses. In the optimum case, currently available wind turbines can convert a maximum of around 45% of the wind capacity into usable electrical power.
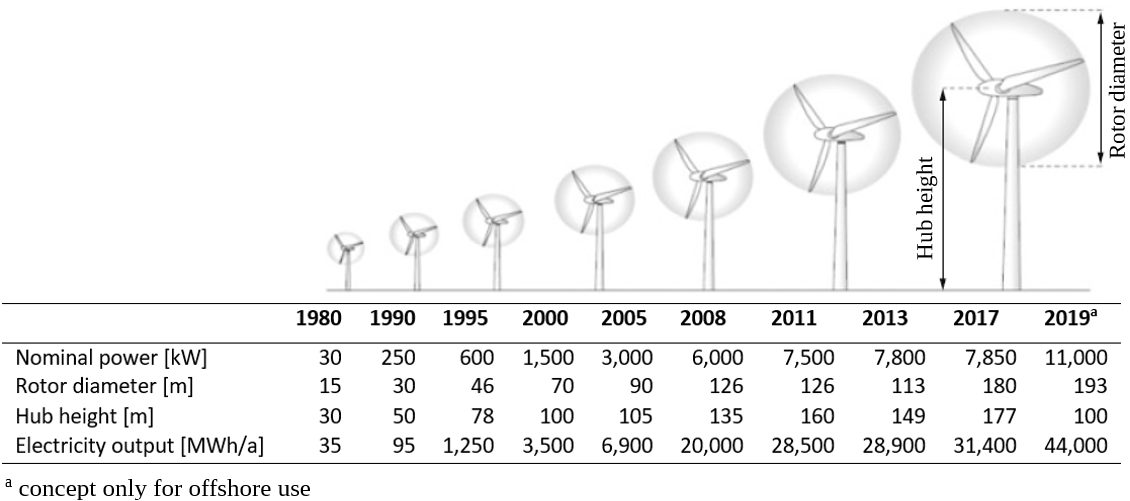
The nominal power is an essential characteristic value for wind turbines and describes the electrical power output at the designated wind speed. In recent years, the nominal power of wind turbines available on the market has increased considerably. Meanwhile, turbines with a rated output of over 10 MW are being offered. However, turbines in the double-digit MW range are only installed offshore, i.e. at sea.