2.1 Hydrogen and different Hydrogen Production models
This chapter provides an overview of hydrogen and its role in mitigating climate change. It covers different methods of hydrogen production and compares their CO2 emissions. The importance of green hydrogen in the energy transition and greenhouse gas reduction is discussed, along with the basics of generating electricity from renewable sources for green hydrogen production. The chapter also explores technical details of green hydrogen production via electrolysis, including comparisons of electrolysis technologies and examples of electrolysers in operation or planned in Northern Germany.
Different types of hydrogen
As stated in the table above, hydrogen in its molecular form rarely occurs in nature and is chiefly found in chemical bonds. Therefore, production processes are necessary to yield pure hydrogen. Both different primary materials and different processes are used to generate hydrogen.
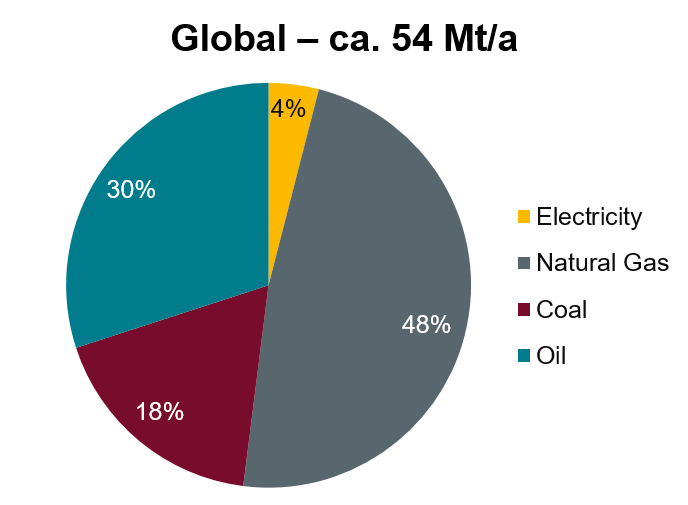
Today, as highlighted in the pie chart below, most of the globally produced hydrogen originates from natural gas (about 48 %). Hydrogen production from coal amounts to 18 % and 30 % of dedicated hydrogen production is from Oil. The remaining 4 % are produced from electricity with respect to water electrolysis. However, as stated in the previous chapter, this ratio has to change in the future, if emission-free hydrogen should contribute to achieving the climate targets.