3. Plant-based pharmaceuticals
3. Plant-based pharmaceuticals
In this book you will learn about the different groups of active ingredients and procedures.
3.2 Process for the extraction of active plant ingredients
Active plant ingredients that are contained in different parts of the plant are mixtures of solids (plant parts), sometimes also mixtures of solids and liquids (e.g. soft fruits). There are suitable separation processes for each of these mixtures.
If you would like to get an initial general overview of physical-chemical separation processes, you will find a good overview here:
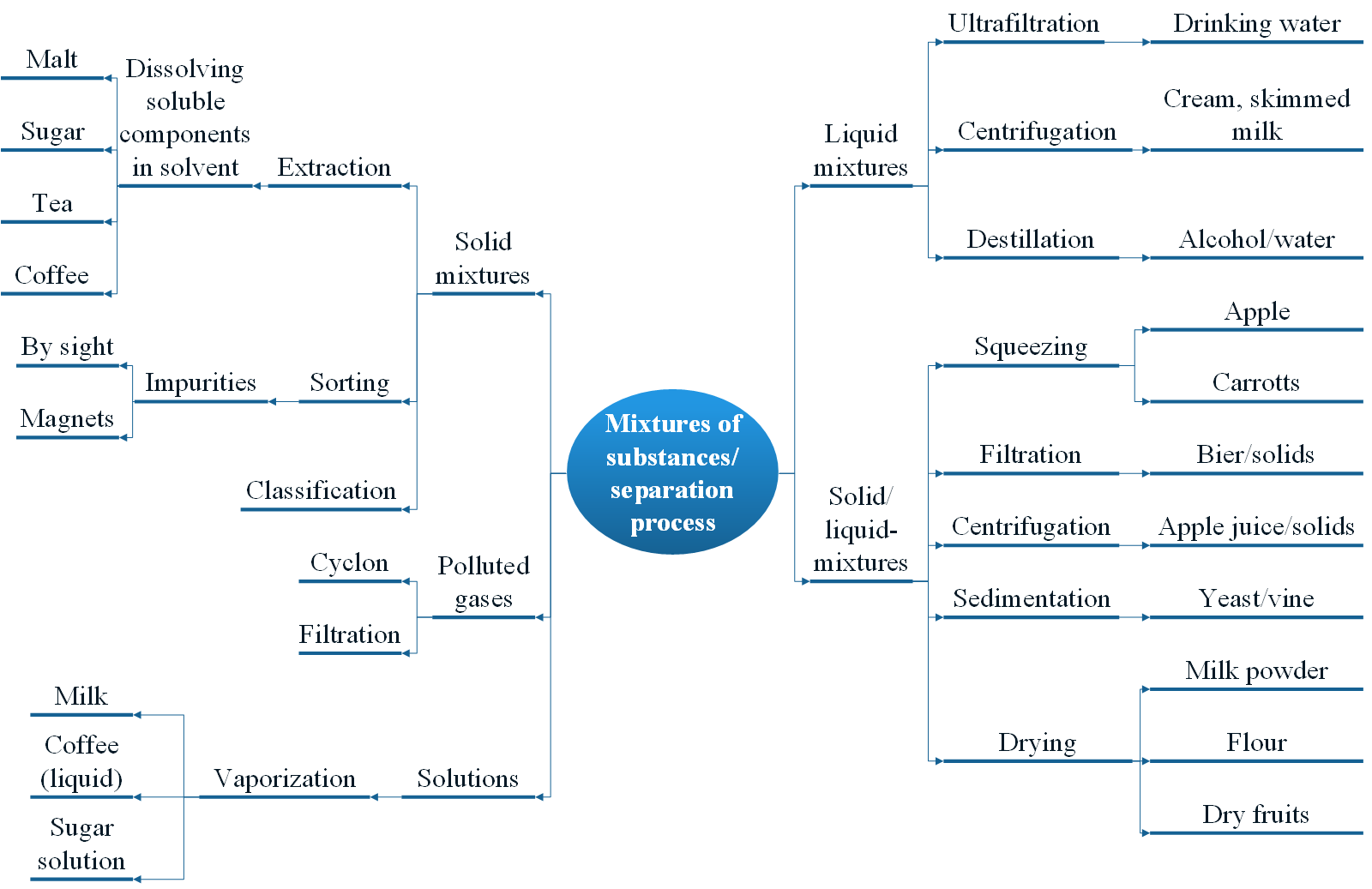
Active plant ingredients are usually obtained by extraction processes. Pressing is suitable for solid-liquid mixtures such as fruits containing oil or juice. For the most part, the entire mixture of substances is extracted from the plants.
If you would like to find out more about the mechanisms of the various separation processes, you can watch this video.
Extraction
Separation of a component of a mixture of solids using a solvent. It is based on different solubilities of the substances to be separated.
It is often a multi-stage extraction and purification process. Unwanted ingredients are removed and the desired active ingredients are enriched.
Suitable solvents are, depending on the properties of the substance to be extracted:
- Water
- Alcohol
- Oils
- Subercritical carbondioxide
General process steps
In the first step, it is usually advisable to crush the extraction material in order to break down the plant cells and increase the surface area on which the solvent can act. This is followed by intensive mixing of the substance mixture and solvent. The substance to be dissolved accumulates in the solvent. After several extraction passes, two different phases are obtained. The extract consists of the solvent mixed with the extracted substance and a residue called raffinate.
If both phases have a large difference in density, they can be separated from each other using a filter or separating funnel, for example. If they are homogeneously mixed, the solvent and extract can also be separated again by distillation or rectification (several distillations in succession). Both substances should have a significantly different boiling point.
Several dissolution and separation steps are often required to obtain pure substances. The following is a brief description of an extraction process commonly used in the pharmaceutical-technical field.
Overview of extraction processes
Percolation
Percolation is used when the solvent can flow easily through the extraction material.
A warm solvent is passed through the plant parts. The brewing of coffee in a coffee filter is usually cited here as an illustrative example. Several percolators connected in series are called repercolation.
Maceration
Also called cold extract. The plant parts are placed in the solvent (water, oil, alcohol) and left to infuse for some time. The soluble components pass into the solvent (macerate).
If the process is carried out at higher temperatures, it is called digestion.
Digestion
The shredded plant material is mixed with the solvent while heat is applied. Over time, the non-soluble components settle to the bottom. The solids and the extract are separated by decanting or filtering.
Here, too, there is an illustrative example from the world of coffee preparation. Brewing coffee using a French press pot corresponds to the principle of digestion. The hot water (solvent) is completely mixed with the extraction material (coffee) and only separated again after a while. The solvent is thus concentrated further and further with the extract substances. However, this also means that the extraction process becomes slower and slower as the concentration of the extract in the solution increases, meaning that completely different substances are dissolved from the extraction material than if the solvent is always fresh. The process must therefore be stopped by separating the extract from the solvent. Decanters (solid bowl screw centrifuge) can be used for this purpose. The suspension rotates in the horizontal bowl, as in a centrifuge. The deposited solids are continuously conveyed outwards by a screw.
In general, centrifuging is a suitable separation process for solid-liquid mixtures and you can take a closer look at the principle of a decanter here: ProjektWiki on decanter
Technically more advanced processes allow, for example, better mixing of the solids and the solvent using agitators, such as in turbo or vortex extraction. The use of ultrasound also causes the extraction mixture to vibrate and thus ensures more intensive mixing during extraction.
The desired components can also be extracted by boiling, provided they are heat-resistant. Plant dyes, for example, can be obtained in this way.
An experiment on this is described here: Abpflanz.PDF
Destillation
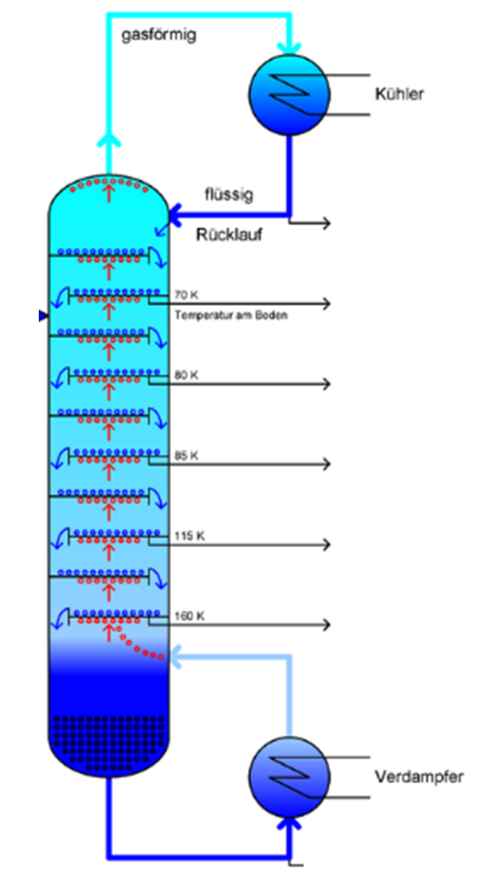
Essential oils or hydrolates (plant water) are often obtained by distillation. Water is mixed with the plant parts and heated. The vapor is collected, cooled in a condenser and thus becomes liquid again. This liquid condensate contains the dissolved plant ingredients and is collected. By repeating the process several times, the concentration of the extracted substances in the distillate can be increased. Large-scale plants use so-called rectification columns, in which the distillation process is repeated continuously as the steam rises and the condensate flows downwards.
Soxhlet extraction
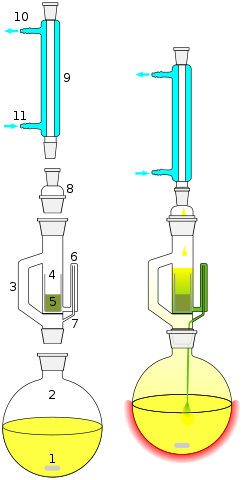
A laboratory process that enables and refines the extraction of soluble substances from solids through a combination of distillation and percolation is the Soxhlet process using a Soxhlet apparatus.
- The solid is filled into the attachment (5)
- Solvent is heated underneath (1)
- Steam rises in the steam pipe (3) condenses (9) and drips through the attachment into the solids
- When a certain filling level is reached, the solvent, which in the meantime has dissolved some of the solid, overflows into the thin tube (6) and back into the flask.
- Gradually, more and more of the dissolved substance accumulates in the flask until finally all the solvent has evaporated
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Beim Abspielen wird eine Verbindung zu den Servern von YouTube hergestellt und der Anbieter kann Cookies einsetzen, die Hinweise über dein Nutzungsverhalten sammeln.
Column chromatography
A tall glass column is used here, which is filled with a solid or powdery packing material. This packing material is called the stationary phase and usually consists of silica gels, aluminum oxide or calcium carbonate, sometimes also of porous, synthetic polymers. It can fill the entire column or only cover the inner surfaces. There is a tap at the bottom of the column. The plant material dissolved in a suitable solvent (acetone, hexane, ethanol, methanol, etc.) is applied to the column. This mixture is called the mobile phase. In order to transport it through the column, a so-called running agent is continuously dripped on from above. Different polarities of the substances in the mobile phase cause interactions with the stationary phase. These cause the mobile phase to separate, as the substances migrate through the solid at different speeds. They separate in zones and can be discharged individually.
Column chromatography can also be used as an analytical instrument by determining and measuring the individual components of the mixture after separation.
On a commercial scale, the process is accelerated by forcing the mobile phase through the stationary phase under pressure.
This video in the Lecture2Go series from the University of Hamburg explains the column chromatography process in detail:
Video Lecture2Go: Naturstoffe - SäulenchromatographieHigh-pressure gas extraction
The extraction of solids can also be carried out with a supercritical fluid instead of liquid organic solvents. This is particularly helpful in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, as there is no need to work with solvents that are sometimes toxic or harmful to health. The process uses so-called supercritical carbon dioxide (CO₂), which assumes a state between gas and liquid under high pressure and high temperature. With the help of a pump or a compressor, the heated CO₂ is passed through the plant material and dissolves the desired substances. The extract is separated in a separator by expanding the CO₂. The process is particularly suitable for low-volatility but thermally unstable substances.