2. Resources for the bioeconomy
2. Resources for the bioeconomy
Abschlussbedingungen
Anzeigen
This book provides an overview of the diverse raw material base of the bioeconomy.
2.1 Plant origin
Plants break down organic substances (carbohydrates, fats, proteins) from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis with the help of sunlight. As primary producers, plants are therefore the most important source of raw materials in the bioeconomy. Plant parts and their fruits are mainly used as food and animal feed, but are also processed to produce building materials, textiles, energy, pharmaceuticals and paper.
The 10 crops with the largest harvested quantities worldwide are sugar cane, maize, wheat, rice, oil palms, potatoes, soybeans, cassava and vegetables (FAOSTAT 2022). Sugar cane, maize, rice and wheat account for half of global primary agricultural production. These crops are mainly grown as food sources. However, sugar cane, maize, palm oil, soy and wheat are also increasingly being used as raw materials for fuel production. Overall, the global cultivation of primary crops, oil plants, fruit and vegetables has risen sharply in the last twenty years (FAO 2022).
Agricultural Plantation
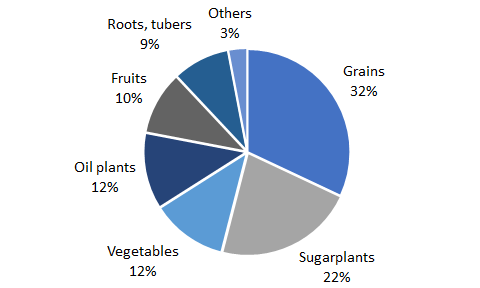
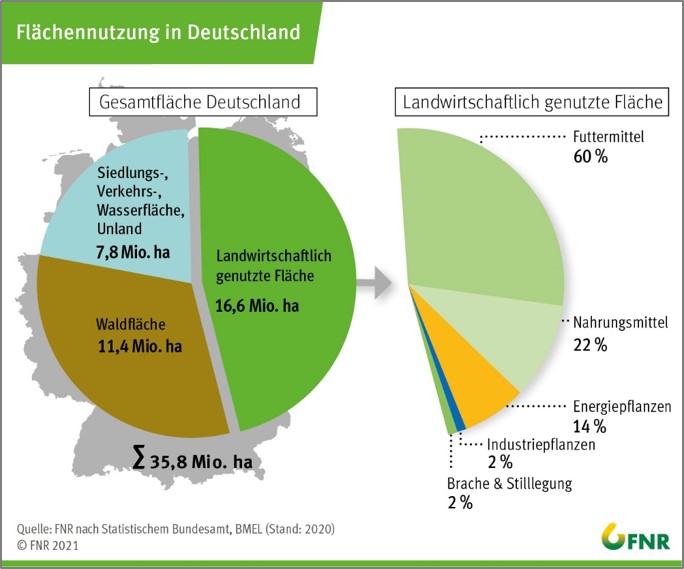
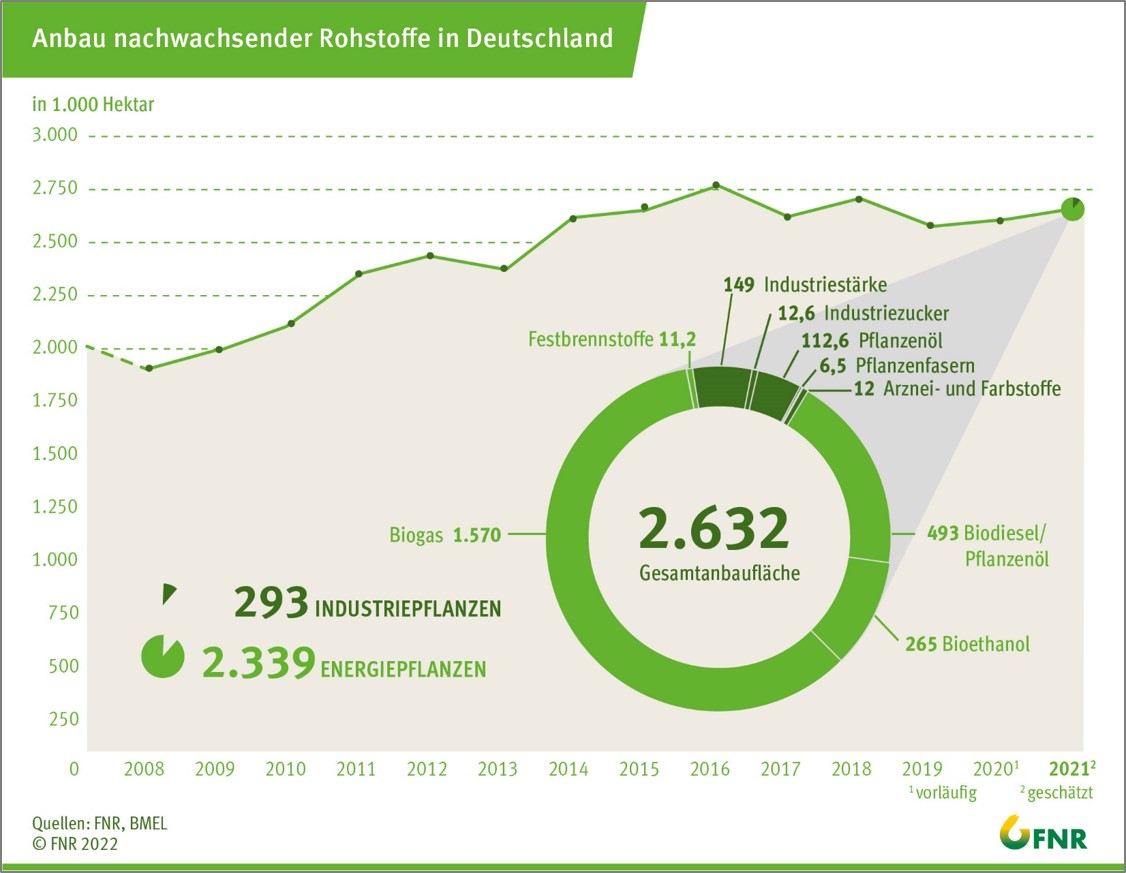
Agricultural crops containing sugar and starch make up the majority of crops grown worldwide. The four crops sugar cane, maize, rice and wheat produce half of the global harvest. In 2021, 9.5 billion tons of crops were produced worldwide (FAO 2022). The following diagram shows the distribution of the various crop groups.
https://www.fnr.de/ftp/pdf/berichte/22004416.pdf
Important plant groups
A distinction can be made on the basis of the mainly used organic ingredients of the plants:- Sugar and starch-containing plants
- Protein-containing plants
- Oil-containing plants
- Lignocellulosic plants
- Medical plants, cosmetically used plants
This article provides an overview of which agricultural waste and by-products can be used for biorefinery processes: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenrg.2020.00152/full
