Biofuels from Lignocellulosic Biomass
Water gas shift reaction
Water gas shift reaction can be used for product gas conditioning. A gas consisting mainly of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) is called “water gas”. "Shift” means to change the ratio of carbon monoxide to hydrogen. The ratio can be increased by adding CO2 or reduced by adding steam.
The water gas shift reaction (WGSR) can be used to adjust the CO/H2 ratio in synthesis gas, i.e. to reduce the carbon monoxide content (see upgrading) or to produce hydrogen. During WGSR carbon monoxide reacts with water vapour to carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The following equation shows the water gas shift reaction, also known as conversion equilibrium:
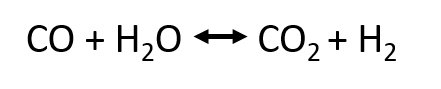
Equilibrium of water gas shift reaction by Anne Rödl (CC0)
The reaction is moderately exothermic and reversible. As the temperature increases, the chemical equilibrium shifts from reaction products to reaction reducts and the speed of the reaction increases. Further, the reaction shifts towards carbon monoxide as temperature increases. The equilibrium for H2 production is favored by high moisture content and low temperatures. Different catalysts are used for low temperature shift (200-250°C) and high temperature shift (350-500°C). Chromium or copper promoted iron-based catalysts are used for high temperature shift and low temperature shift deploys a copper-zinc-aluminum catalyst.
WGSR is also used in steam reforming processes to elevate the hydrogen content.