1. What is bioeconomy?
1. What is bioeconomy?
Completion requirements
View
This book contains all basic information on bioeconomy.
1. What is bioeconomy?
What you should know:
- The bioeconomy encompasses the economic sectors that produce, use or process bio-based raw materials
- The term bioeconomy emerged from a political program to promote innovation in the industrial use of renewable resources
- 17 countries have their own bioeconomy strategy
The bioeconomy
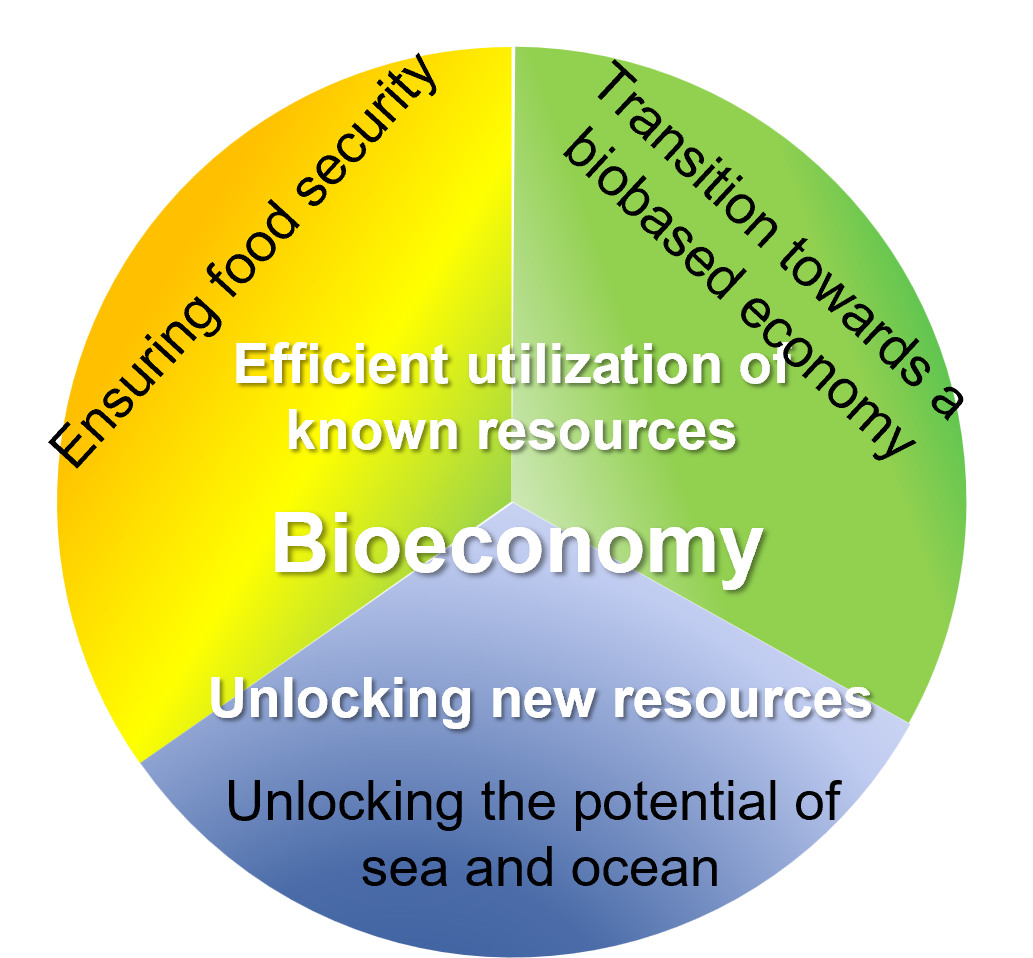
The bioeconomy encompasses the primary production sectors (agriculture, forestry and fisheries) as well as industries that use or process bio-based raw materials, such as the pulp and paper industry, food industry, wood processing industry, chemical and pharmaceutical industry, biotechnology and parts of the energy industry. In a revised version of the bioeconomy strategy from 2018, services that use biological resources and processes are now also included in the bioeconomy (e.g. tourism, transportation or architecture).
The five goals of the bioeconomy (see also figure below) are:
- Ensuring food and nutrition security
- Sustainable management of natural resources
- Reducing dependence on non-renewable and non sustainable - domestic or non-domestic - resources
- Climate protection and adaptation to climate change
- Creating jobs and maintaining European competitiveness
The concept of bioeconomy is also seen in the context of social change towards a post-industrial society. The focus here is on the transition from a fossil-based economy to a bio-based economy. It is about the optimal use of renewable raw materials by minimizing waste and losses, but also about expanding the raw material base by tapping into previously unused resources such as waste and residual materials. The bioeconomy also follows the approach of a circular economy with virtually infinite availability of resources. In reality, however, there are natural limits, as land, water and freshwater resources, for example, are not infinitely available.
Conditions for the advancement of the bioeconomy are:
- natural resources
- Labor resources
- Knowledge resources
- Capital resources
- Infrastructure
The learning material provided here focuses primarily on natural resources, knowledge and, to some extent, the necessary infrastructure for the bioeconomy.