2.3 Green Hydrogen Production via Electrolysis
| Website: | Hamburg Open Online University |
| Kurs: | Green Hydrogen |
| Buch: | 2.3 Green Hydrogen Production via Electrolysis |
| Gedruckt von: | Gast |
| Datum: | Freitag, 13. März 2026, 09:24 |
Electrolytic splitting of water - Basics
As already mentioned in chapter 2.1, green hydrogen is produced via the process of electrolytic splitting of water. Beside an electrolyser, renewably generated electricity and a hydrogen containing substance such as water is needed. The electrolysis is by no means a newly developed technology, but rather a process that was first described already over 200 years ago. After the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta developed the first powerful battery in 1799, a year later various researchers succeeded in demonstrating the electrolytic splitting of water with the help of this first reliable voltage source. Among others, the scientist Johann Wilhelm Ritter (1776-1810 in Germany) conducted an experiment in which electric current was used to produce a redox reaction - the first electrolyser was invented. Ritter was able to prove, that hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) are produced in a ratio of 2:1. A sketch of Johann Wilhelm Ritter's simple electrolyser is illustrated below.
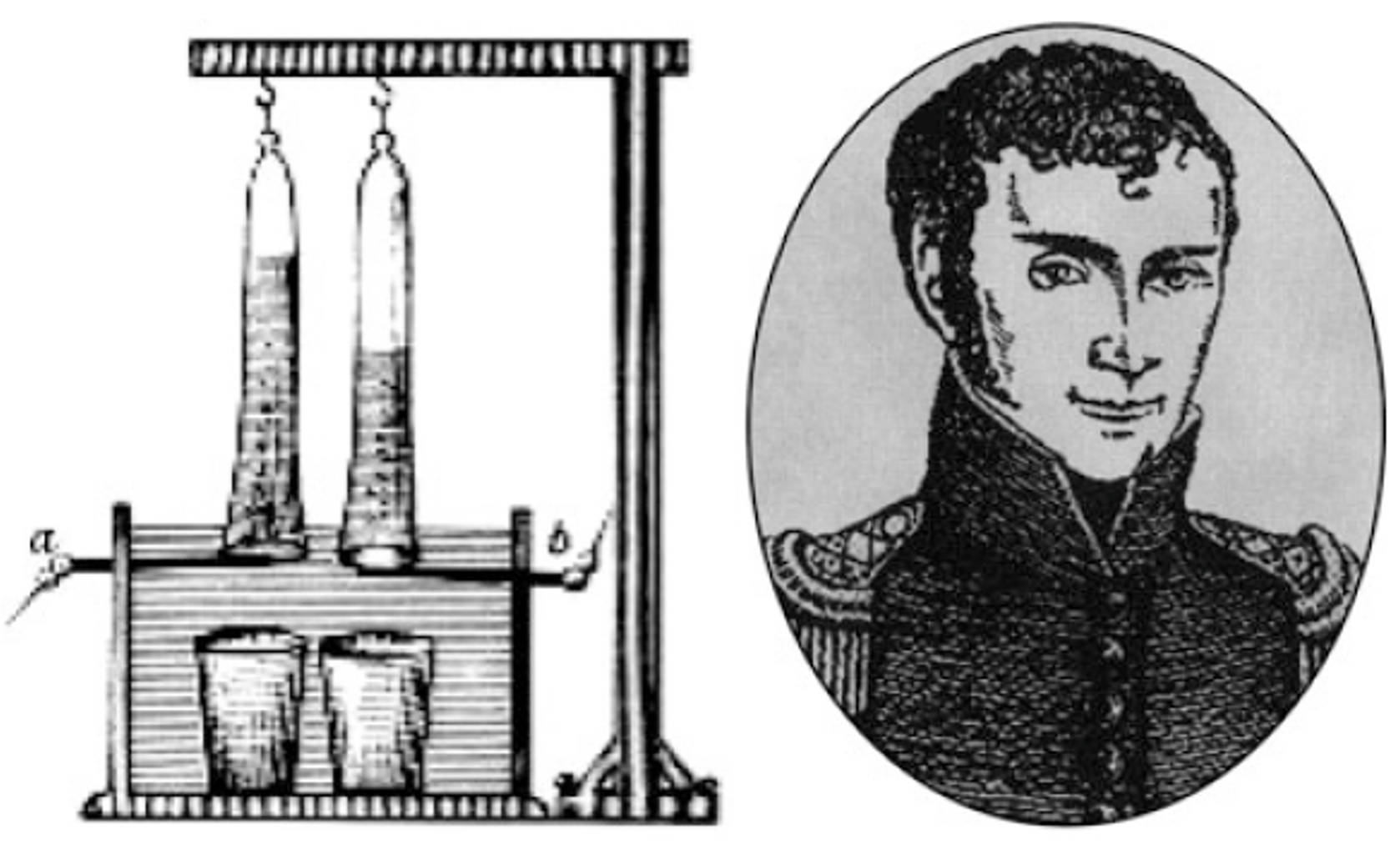
2 H2O + electrical energy --> 2 H2 + O2
There are different variants for electrolysis, which differ in their process engineering design. All electrolysis processes have the following in common:
At the anode an electrochemic oxidation takes place and oxygen is released.
At the cathode an electrochemic reduction takes place. The hydrogen is released.
The charge exchange that becomes necessary between the electrodes takes place via an ion-conducting electrolyte.