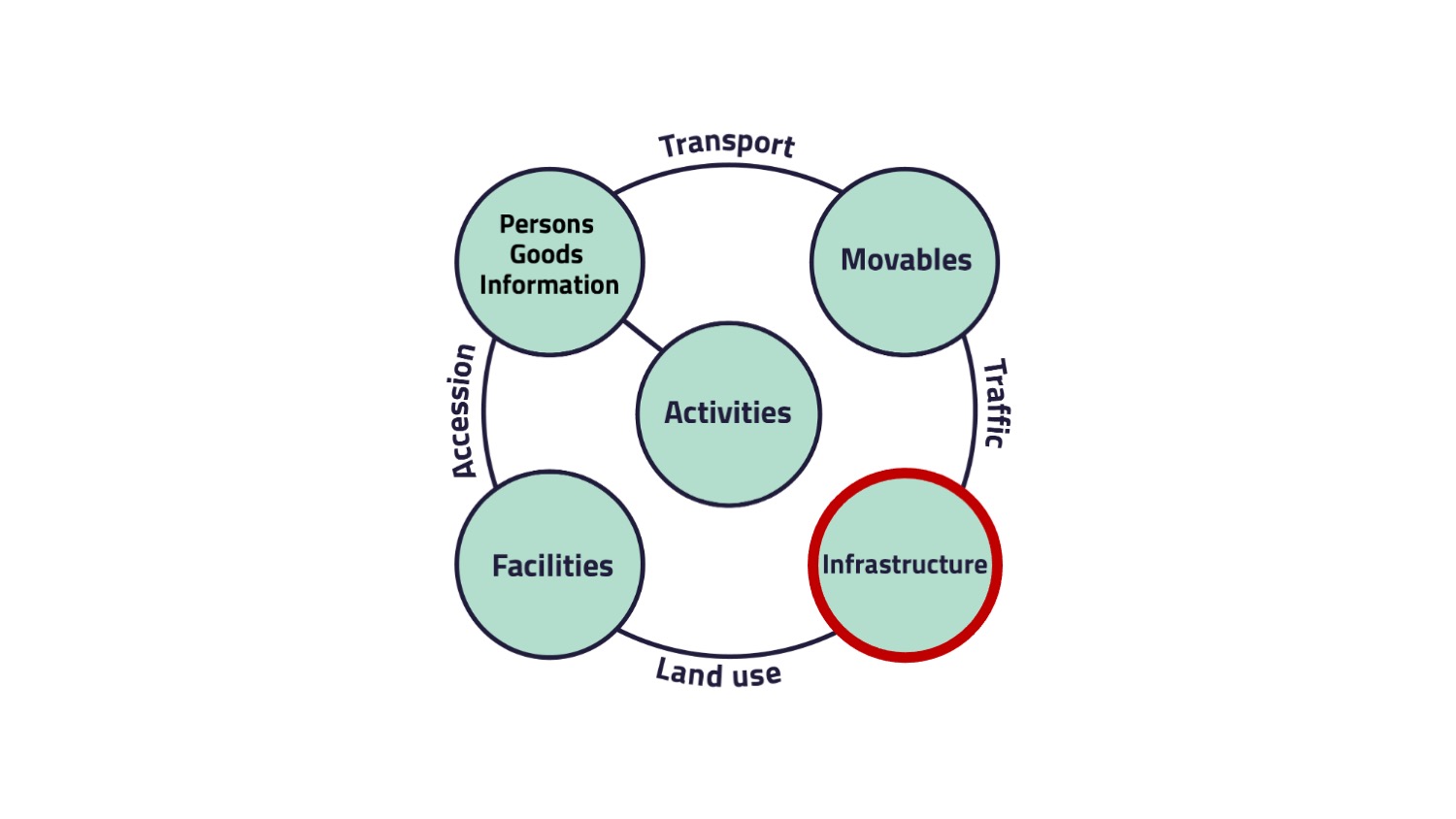
Conceptual System Model of Transport and Traffic
5. Infrastructure
After you got to know more about the three elements before, this chapter will give you more information about the element „Infrastructure“. In the following MoGoLo topic cluster, this will be differentiated depending on the mode of transport.
Infrastructure is the underlying (invisible) structure of a human society and is often assumed to be limited to publicly accessible space, such as schools, theatres, sports arenas, roads, railways, paths in the wilderness etc.. Besides that, infrastructure often means our systems of roads, railways, airports and harbours.
In academic language this is a too narrow interpretation that neglects the abstract dimension of the concept. Therefore, in the further topic cluster the following definition is used:
The transportation infrastructure is limited to enabling flows of persons and goods and in a wider concept data as well.
Examples for infrastructure:
- streets/road
- railways
- waterways
- air corridors
- pipe lines
- data lines
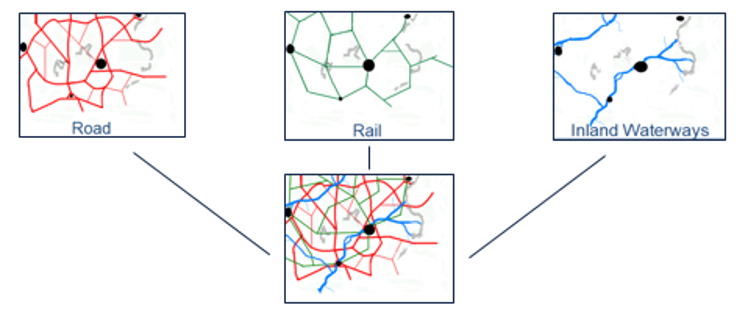
Infrastructure network
Various infrastructures form a large infrastructure network, which can be seen in the figure "Network structure". You can see different kind of networks for the road, rail and water infrastructure. The combination of all three networks forms the transportation infrastructure.
The connection between infrastructure and facilities is called land use.
Land use
Land use
- is the location of facilities at specific sites.
- is the combined result of public planning and complex market mechanisms.
- may be seen as an interaction between a planned facility and infrastructure in its widest sense.
- results in giving the facility a permanent address.
Literature
Flämig, H.; Sjöstedt, L.; Hertel, C. (2002): Multimodal Transport: An Integrated Element for Last-Mile-Solutions? In: Conference Proceeding of the International Conference “Freight Transport Automation and Multimodality. Organisational and Technological Innovations,Delft, Niederlande